Archives
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-04
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-11
- 2018-10
- 2018-07
-
A localization of GK to
2022-08-26
A localization of GK to both a cytoplasmic and perinuclear area of normal rat pancreatic beta-cells was reported in 1996 (Noma et al., 1996), which changed on acute hyperglycemia to a more diffuse staining throughout the cytoplasm. The localization of GK within the nucleus was first reported by Mura
-
br Indirect GLI antagonists br Direct GLI antagonists br
2022-08-25
Indirect GLI antagonists Direct GLI antagonists Concluding remarks Targeting GLI effectors represents a promising therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment. This is particularly relevant for certain tumors, such as MB, since, although classified into four distinct molecular groups (Hh- or W
-
br Discussion According to the
2022-08-25
Discussion According to the generally accepted notion which originated from the study of ATP-depleted tipiracil the changes in Ca2+ homeostasis induced by ATP depletion and leading to the activation of the Gárdos effect are due to the inhibition of Ca2+ pumping, and the subsequent entry of Ca2+ t
-
Ionotropic aminobutyric acid GABA receptors GABARs belong to
2022-08-25
Ionotropic γ-aminobutyric G-1 (GABA) receptors (GABARs) belong to the Cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel (LGIC) superfamily and play an important role in the rapid inhibitory synaptic transmission in nervous systems of both vertebrate and invertebrate (Buckingham et al., 2005). Insect ionotropic GABA
-
br Acknowledgements The authors have no ethical conflicts
2022-08-25
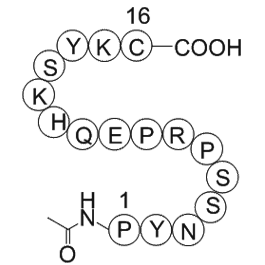
Acknowledgements The authors have no ethical conflicts to disclose. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. This work was funded by the Research Council of Lithuania. Introduction This paper studies whether there is a causal influence of the risk-taking incentives provided by op
-
We sought to deduce the role of membrane
2022-08-24
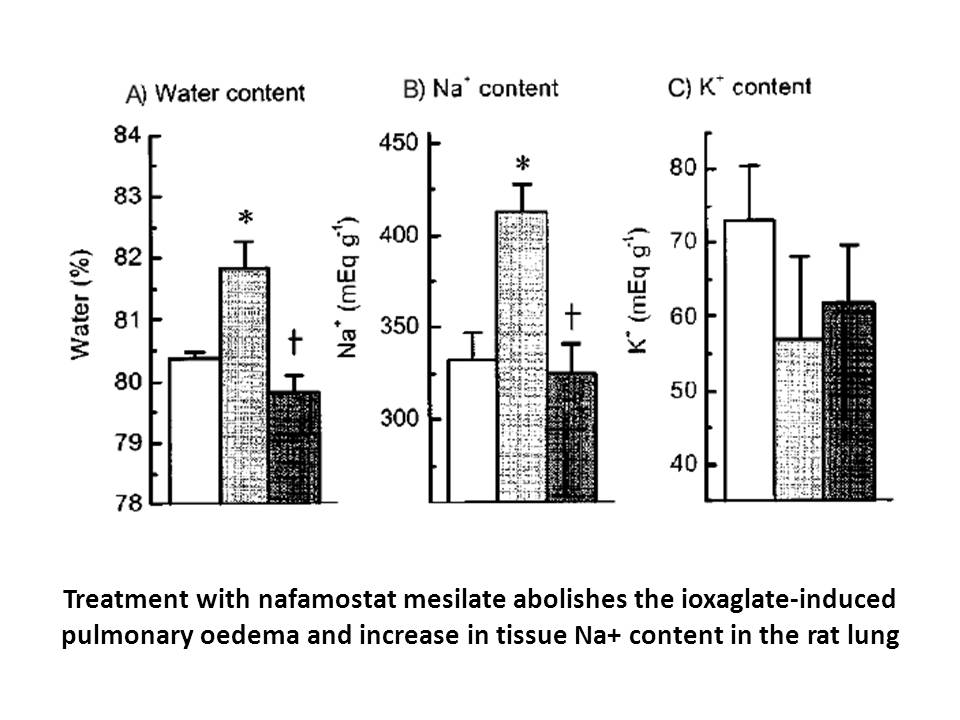
We sought to deduce the role of membrane lipid determinants on endo- and exocytosis by applying a combination of metabolic (lipid) engineering approaches and biophysical methods, e.g. classical optical imaging technologies and high-resolution time-resolved patch-clamp/capacitance measurements. The l
-
br Acknowledgments br Introduction Lung cancer
2022-08-24
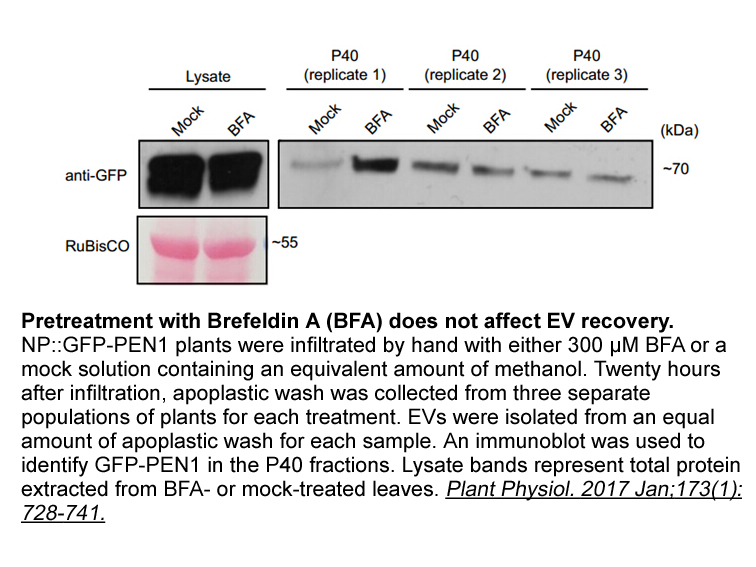
Acknowledgments Introduction Lung cancer is a common but extremely perilous cancer, with approximately 733,000 new incidences reported annually in China [1]. Lung cancer ranks highest in the causes of tumor-related mortality, accounting for approximately one quarter of all cancer deaths [2]. N
-
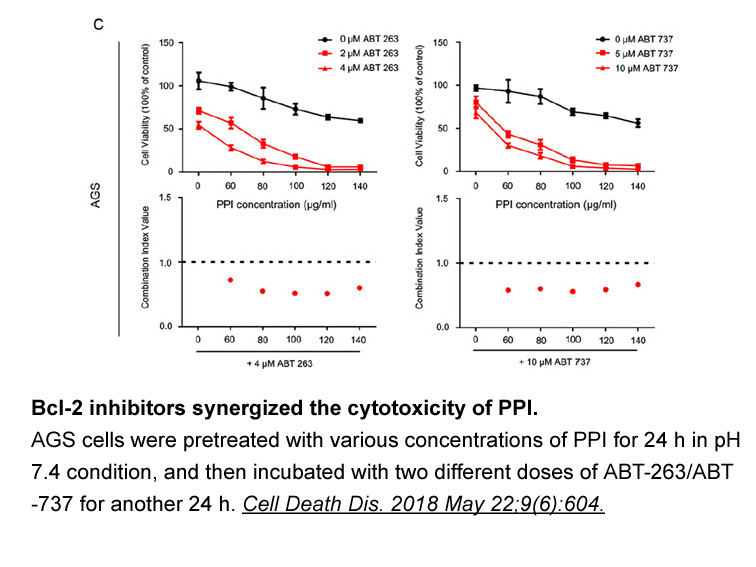
The Bcl and Bcl xL genes
2022-08-24

The Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL genes contain the CRE binding site in their promoter regions for CREB and CBP to bind to, so CREB phosphorylation was shown to up-regulate these anti-apoptotic genes, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL [[29], [30], [31]]. Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL prevent the activation of caspases and the release of mito
-
uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation Acknowledgments Fina
2022-08-24
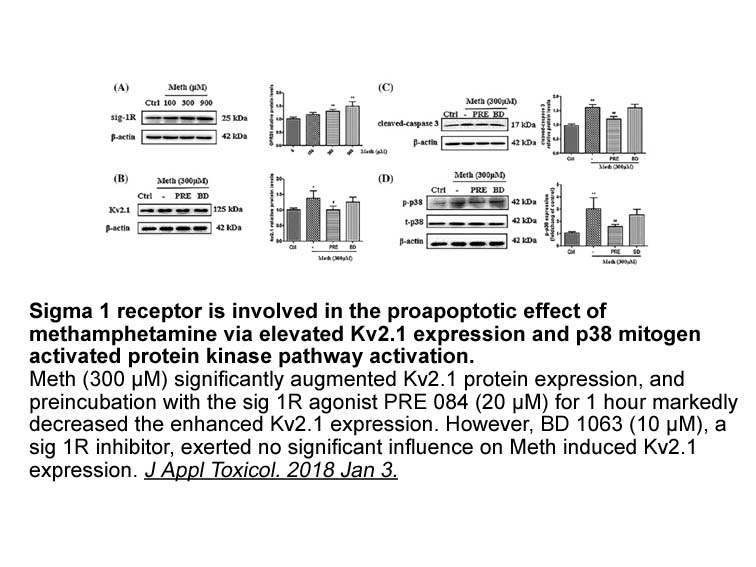
Acknowledgments Financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81730094, 81473262 and 81573299) is gratefully acknowledged. This project was also supported by the “111 Project” from the Ministry of Education of China, the State Administration of Foreign Expert Affairs of C
-
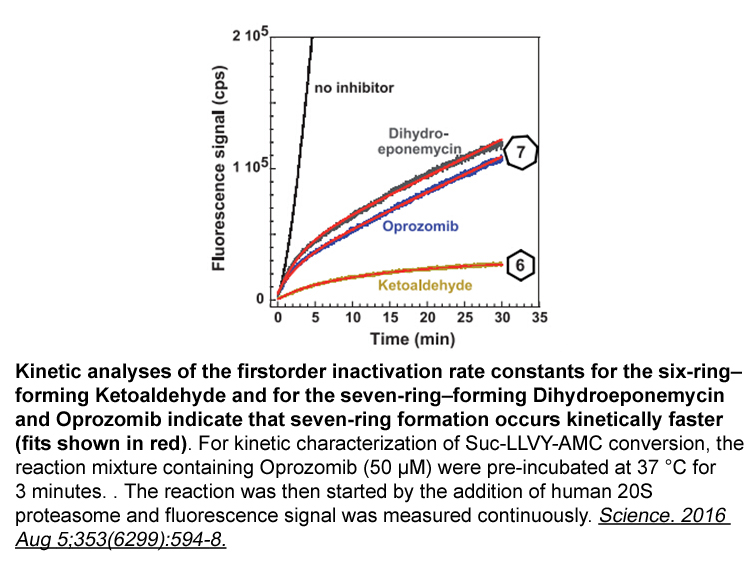
In our study we evaluated adenovirus type Ad as
2022-08-24
In our study we evaluated adenovirus type 5 (Ad5) as a vehicle for delivering Cre recombinase in conditional transgenic mouse based on the Cre-loxP system, in order to achieve GlyT1 gene modulation in a specific thalamic region in the adult animal. GlyT1 is a sodium- and chloride-coupled glycine tra
-
In three groups independently proposed two different
2022-08-24
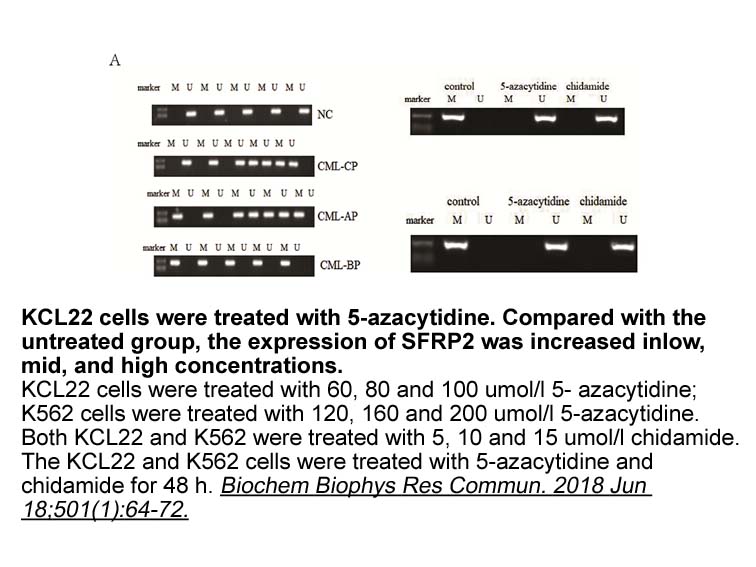
In 2001, three groups independently proposed two different mechanisms for the catalytic reaction of GlxI [5], [6], [7]. Richter and Krauss (RK) used HF/4–31G calculations of the active site, coupled with a frozen effective fragment potential description [8], [9] of eleven residues in the binding sit
-
Glutamate activates cationic glutamate gated
2022-08-24
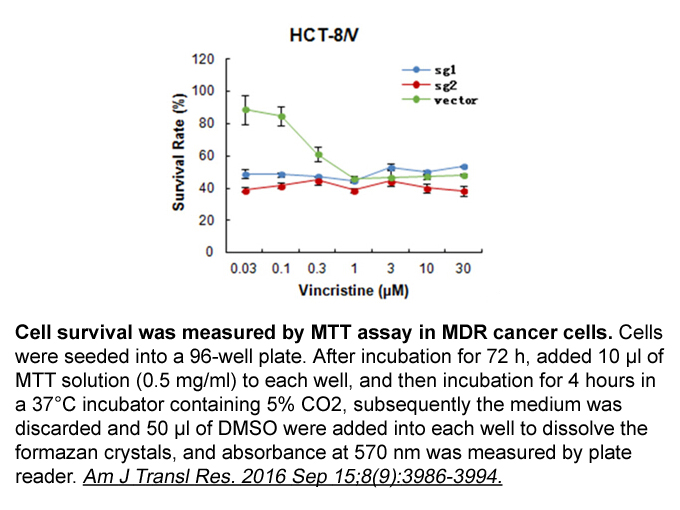
Glutamate activates cationic glutamate-gated channels (i.e. ionotropic glutamate receptors) that mediate the fast excitatory actions of glutamate. It also activate G protein-coupled receptors, named metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) (Pin and Bettler, 2016). The eight subtypes of mGluRs are k
-
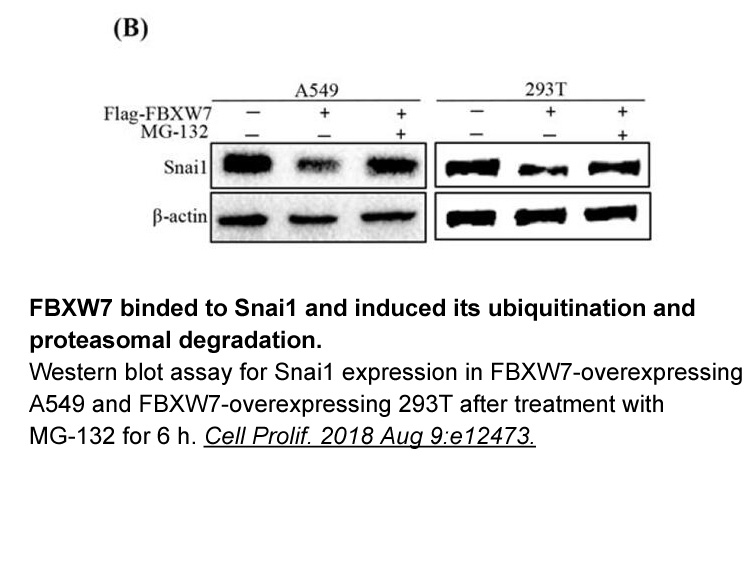
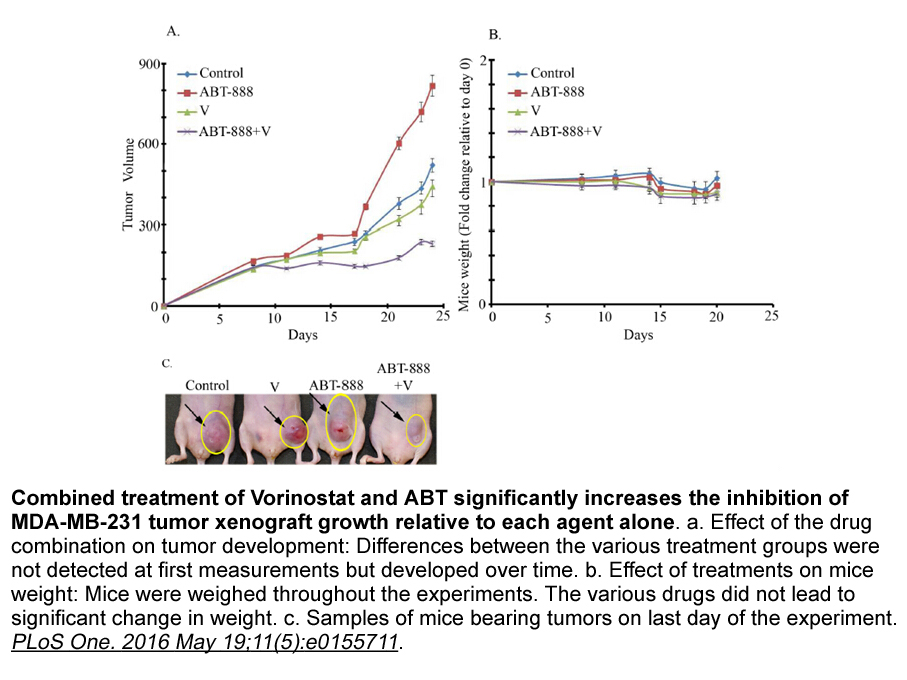
br Conclusions br Acknowledgments This study
2022-08-23
Conclusions Acknowledgments This study was supported by funds from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 31360245, 31460258) and the Applied Basic Research Foundation of Yunnan Province of China (2011FZ111). Introduction Acute myocardial infarction is the undoubted cause o
-
During the course of our optimization of the
2022-08-23
During the course of our optimization of the diarylsulfonamide chemotype as FFA4 agonists, we identified xanthene as a potent and selective antagonist of FFA4 (). Xanthene was able to block the agonist induced intracellular Ca response elicited by both linoleic GDC-0623 sale and compound in comp
-
br Introduction A great many isoprenoids
2022-08-23
Introduction A great many isoprenoids with varieties of structural diversity, such as steroids, carotenoids, prenyl quinones, and natural rubber, occur in nature. All of these biosynthetic precursors are constructed by the action of prenyl chain elongating enzymes [1], [2], [3], [4]. These enzyme
16083 records 387/1073 page Previous Next First page 上5页 386387388389390 下5页 Last page